Overview
Stress or Anxiety is a physiological and psychological response that occurs when individuals perceive an imbalance between the demands placed on them and their ability to cope. This natural reaction triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, involving hormonal changes and heightened alertness to deal with perceived threats or challenges.
Reasons for Anxiety
Anxiety can arise from various sources, including work, relationships, financial pressures, or major life changes. Its effects can range from mild to severe, depending on the intensity and duration of the stressors.
Good (Eustress) vs. Bad (Distress) anxiety
- Motivates us to achieve goals and meet challenges.
- Short-term, enhances focus, concentration, and performance.
- Examples: Roller coaster rides, competitions.
- Harmful to our body, leads to poor concentration, anxiety, and decreased performance.
- Can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
- Chronic stress can cause depression, anxiety, severe headaches, loss of sleep, weight fluctuations, and high blood pressure.
Stress Management
Stress management involves strategies or techniques to reduce anxiety and minimize its negative impacts on our well-being. Effective anxiety management focuses on lifestyle changes that help relax the mind and body, promoting overall health and goal achievement.
The ABC Model of Stress Management
Dr. Albert Ellis’s ABC model of anxiety management emphasizes the importance of our beliefs in shaping our responses to anxiety.
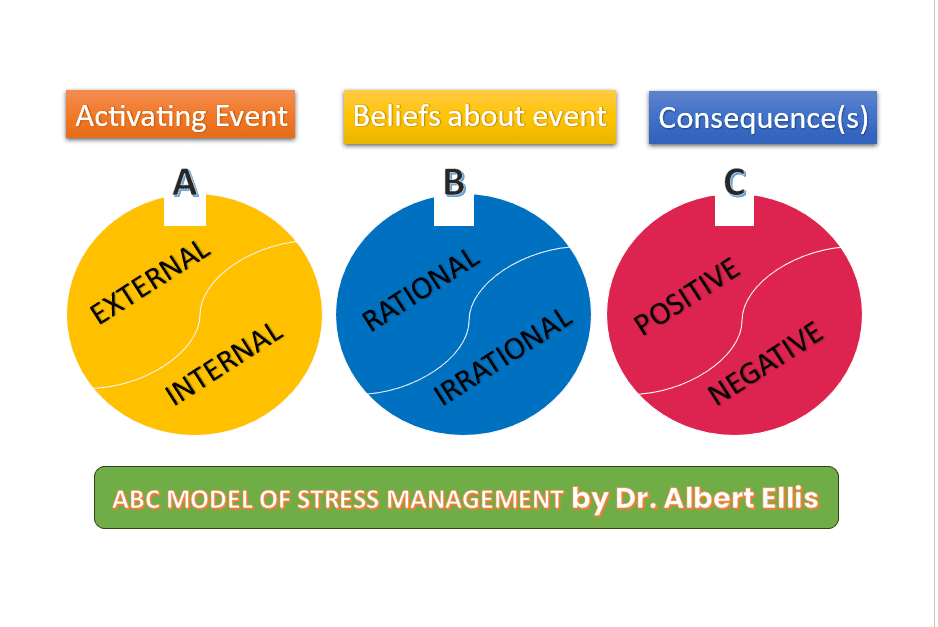
- A: Activating Event – The situation or trigger.
- B: Beliefs – Our thoughts and self-talk regarding the event.
- C: Consequences – Our response to the event.
By changing our beliefs or attitudes towards a situation, we can influence the consequences and manage anxiety more effectively.
Reasons for Anxiety Management
- To maintain good physical and mental health
- To foster healthy relationships
- To improve work efficiency
- To balance mood swings
- To enhance overall quality of life
Stress Management Techniques
1. To-Do Lists:
Organizes tasks, breaking them into manageable steps. Prevents feelings of overwhelm and reduces the risk of forgetting important tasks.
2. Time Management:
Prioritizes tasks as urgent, important, or less important. Helps complete tasks on time and increases productivity.
3. Physical Exercise:
Activities like walking, running, or aerobics boost the production of feel-good hormones. Keeps the mind and body healthy.
4. Meditation:
Focuses the mind to achieve mental clarity and emotional calm. Reverses the impact of anxiety on the mind and body.
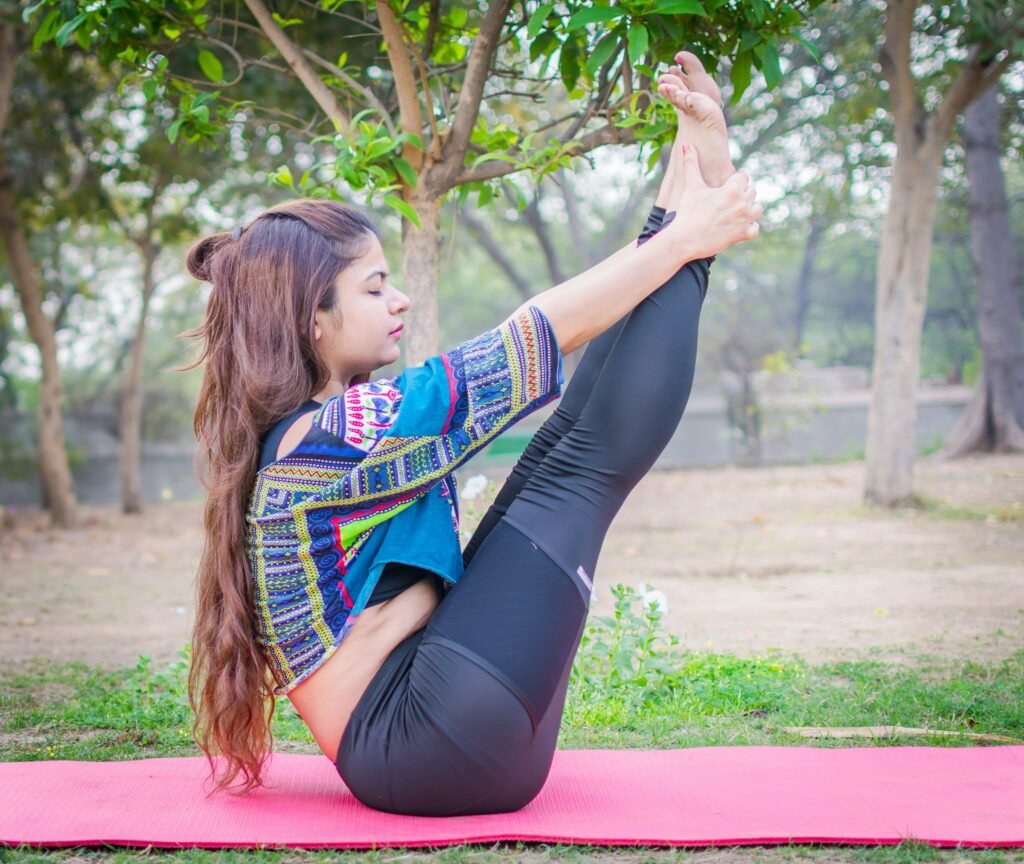
5. Yoga:
Combines breathing techniques, physical postures, and meditation. Promotes physical and mental well-being, reduces anxiety, and improves concentration.
6. Healthy Diet:
Eating balanced meals and staying hydrated supports proper body function and anxiety reduction.
7. Positivity:
Maintaining a positive attitude helps manage anxiety and depression. Encourages tackling situations proactively.
8. Good Sleep:
Ensures regular sleep patterns to avoid mood swings and enhance concentration.
9. Spending Time with Family and Friends:
Taking breaks and enjoying time with loved ones helps relax and reduce anxiety.
10. Nature Walks:
Walking in nature and breathing fresh air can significantly lower anxiety levels.
Anxiety Management for Students
- Time Management: Creating a timetable with short-term and long-term goals.
- Physical Exercise: Engaging in activities like walking or playing sports.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming fruits, vegetables, and sufficient water while avoiding junk food.
- Yoga and Meditation: Practices to enhance physical and emotional well-being and improve concentration.
- Spending Time with Loved Ones: Relaxing with friends and family to manage stress.
- Positive Thinking: Maintaining a positive attitude towards challenges.
- Self-Reliance: Building confidence and responsibility through independent work.

Importance of Working Independently
- Increased Learning: Encourages the use of strengths and skills.
- Responsibility and Empowerment: Instills discipline and work ethics.
- Creativity and Satisfaction: Promotes innovative thinking and problem-solving.
- Accountability: Enhances productivity and positive interactions.
Practical Ways to Overcome anxiety
- Goal Achievement: A stress-free mind improves concentration and performance.
- Boosting the Immune System: Managing anxiety strengthens the immune system.
- Enhancing Well-being: Encourages positive reactions to stress and improves mental and physical health.
- Developing Problem-Solving Skills: Fosters rational thinking and clear perception.
- Preventing Psychological Issues: Helps tackle emotional and physical traumas, leading to healthy relationships.
By integrating these anxiety management techniques into daily life, individuals can significantly reduce the negative impacts of anxiety and improve their overall quality of life.
1. What is stress or anxiety?
Anxiety is a physiological and psychological response that occurs when individuals perceive an imbalance between the demands placed on them and their ability to cope. This natural reaction triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, involving hormonal changes and heightened alertness to deal with perceived threats or challenges.
2. What is Anxiety management?
Stress management refers to the techniques and strategies used to control, reduce, and cope with anxiety in daily life. It involves identifying stress triggers, developing healthier coping mechanisms, and fostering resilience.
3. Why is stress management important?
Effective stress management is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and reducing the risk of physical and mental health problems associated with chronic anxiety. It helps individuals maintain focus, productivity, and emotional balance.
4. What are some common signs of stress?
Signs of anxiety can include physical symptoms like headaches, muscle tension, and fatigue, as well as emotional symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and mood swings. Behavioral changes like changes in appetite or sleep patterns can also indicate anxiety.
5. How can I reduce anxiety at work?
To reduce anxiety at work, it’s important to prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and establish boundaries between work and personal life. Effective communication with colleagues and supervisors, taking regular breaks, and practicing mindfulness can also help manage workplace anxiety.
6. When should I seek professional help for stress?
If stress becomes overwhelming or begins to significantly impact your daily life, relationships, or work performance, it may be beneficial to seek help from a mental health professional. They can provide guidance, support, and personalized strategies to manage anxiety effectively.
7. How can I create a anxiety management plan?
Creating a anxiety management plan involves identifying your anxiety triggers, evaluating current coping strategies, and selecting new techniques to incorporate into your routine. Setting realistic goals, prioritizing self-care, and regularly reviewing and adjusting your plan are key to long-term stress management.
8. What are some unhealthy ways people cope with anxiety?
Unhealthy coping mechanisms for anxiety can include substance abuse (such as excessive alcohol or drug use), avoidance of problems or responsibilities, overeating or under-eating, and withdrawing from social interactions. These strategies may provide temporary relief but can worsen anxiety and have negative long-term consequences.
9. How long does it take to see improvements in anxiety levels with effective management?
The time it takes to see improvements in stress levels can vary depending on individual circumstances and the effectiveness of chosen anxiety management techniques. Consistently practicing healthy coping strategies and making lifestyle changes can lead to gradual reduction in anxiety and improved overall well-being over time.





